 |
| 1986 ~ 2025 台幣兌美元匯率歷史圖 |
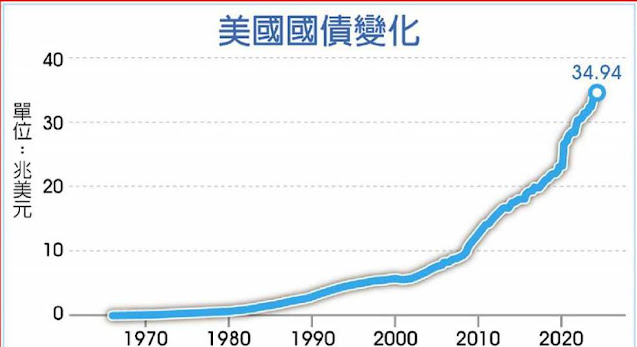 |
今年美國公債到期多,造成美元轉弱 |
Related articles
ETF投資,美股投資,臺股ETF投資,西洋情歌,西洋音樂,閱讀與興趣 [ラブソング, песня любви][ETF inversión, ETF投資します, ETF инвестиции], all investment and interesting stuff I touched, experienced;
 |
| 1986 ~ 2025 台幣兌美元匯率歷史圖 |
 |
今年美國公債到期多,造成美元轉弱 |
 利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool )
利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool ) 川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world )
川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world ) 2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked)
2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked) 如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? )
如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? ) 【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution )
【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution ) 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法
C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法 什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate?
什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate? 豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean
豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司
NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司 歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢
歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢台灣的央行、保險公司、銀行和券商在美國國債的投資總額預估相當可觀,並且這些投資在面對關稅戰和貨幣戰等經濟情況時,具有重要的戰略意義。Taiwan's central bank, insurance companies, banks and securities firms are estimated to have a considerable total investment in U.S. Treasuries, and these investments are of great strategic significance in the face of economic situations such as tariff wars and currency wars.
 |
| 2882 K chart |
央行的投資:Central bank investments
保險公司:Insurance companies
 |
| 2885 K chart |
銀行和券商:Banks and brokerage firms:
根據最新的資料,台灣的保險公司、銀行和券商在美國國債的投資總額預估如下:
在當前的國際經濟環境中,台灣的美國國債投資面臨多重風險,特別是在關稅戰和貨幣戰的背景下,美元會貶值、美公債今年 9.2兆美元要到期 ,特別是6月,約佔到期總額的70%。這些債務的到期將對市場流動性和利率造成壓力,因為政府需要進行再融資以應對這些到期的債務。
,關稅戰讓美公債殖利率高檔震盪:
關稅戰影響:
貨幣戰影響:
市場反應:
總體而言,台灣央行、保險公司、銀行、卷商對美國國債的投資不僅是資產配置的一部分,投資人要盡量避開持有過大美公債的保險公司、銀行、卷商,也是對抗5月半導體關稅、美元貶值、6月美公債到期、利率風險和尋求穩定收益的重要策略。隨著市場環境的變化,這些投資的規模和策略可能會進一步調整,台灣的金融機構在美國國債的投資策略需要靈活應對國際經濟環境的變化,特別是在面對關稅和貨幣政策的不確定性時,應加強風險管理和資產配置的多樣化。
 利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool )
利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool ) 川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world )
川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world ) 2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked)
2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked) 如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? )
如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? ) 【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution )
【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution ) 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法
C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法 什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate?
什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate? 豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean
豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司
NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司 歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢
歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢根據最新的資訊,2025年美國公債到期的情況及川普關稅政策對經濟風險的影響如下:According to the latest information, the maturity of U.S. Treasury bonds in 2025 and the impact of Trump’s tariff policy on economic risks are as follows:
在2025年,美國將面臨大量的公債到期,預計到期的國債總額約為9.2兆美元,這些到期的債務主要集中在上半年,特別是6月,約佔到期總額的70%。這些債務的到期將對市場流動性和利率造成壓力,因為政府需要進行再融資以應對這些到期的債務。In 2025, the United States will face a large amount of public debt maturing, with the total amount of national debt maturing expected to be approximately US$9.2 trillion. These maturing debts are mainly concentrated in the first half of the year, especially June, accounting for about 70% of the total amount maturing. The maturity of these debts will put pressure on market liquidity and interest rates as the government will need to refinance to meet these maturing debts.
具體來說,根據不同的報導,2025年到期的國債數量如下:Specifically, according to various reports, the number of Treasury bonds maturing in 2025 is as follows:
在量化寬鬆(QE)期間,美國聯邦儲備系統(Fed)主要購買了以下幾類金融資產:During quantitative easing (QE), the U.S. Federal Reserve System (Fed) mainly purchased the following types of financial assets:
國債(Treasury Securities):聯儲在QE期間大量購買美國國債,以降低長期利率並促進經濟增長。這些國債包括短期和長期的各類債券。The Fed purchased large amounts of U.S. Treasury bonds during QE in order to lower long-term interest rates and promote economic growth. These government bonds include both short-term and long-term bonds.
抵押擔保證券(Mortgage-Backed Securities, MBS):聯儲還購買了大量的抵押擔保證券,這些證券是由房貸組合而成的,旨在支持住房市場並促進信貸流動性。這些購買行為在2008年金融危機後尤為顯著,聯儲的MBS持有量在高峰時期達到約2.7兆美元。The Fed also purchased large amounts of mortgage-backed securities, which are bundles of mortgage loans, in an effort to support the housing market and facilitate the flow of credit. These purchases were particularly pronounced after the 2008 financial crisis, with the Fed's MBS holdings reaching about $2.7 trillion at their peak.
其他金融資產:在某些QE階段,聯儲也可能購買其他類型的資產,如公司債券等,以進一步支持金融市場的流動性。During certain QE phases, the Fed may also purchase other types of assets, such as corporate bonds, to further support liquidity in financial markets.
聯儲的股東主要是美國的商業銀行。具體來說:The Fed's shareholders are mainly U.S. commercial banks. Specifically:
成員銀行:所有全國性銀行必須成為聯儲系統的成員,並持有其地區聯邦儲備銀行的股份。這些股份的持有是法律要求的,並且不能被交易或作為抵押品使用。成員銀行每年可以獲得最高6%的股息。
股東結構:聯邦儲備銀行的股東包括全國性銀行和選擇成為成員的州立銀行。根據法律,成員銀行必須將其資本的3%作為股份投資於聯邦儲備銀行。這意味著,雖然這些銀行在技術上是聯儲的股東,但他們對貨幣政策的決策並沒有直接控制權。
股東的影響:儘管成員銀行持有股份,但他們的投票權限主要限於選舉聯邦儲備銀行的董事會成員,並不包括對貨幣政策的直接影響。這樣的結構使得聯儲在運作上保持一定的獨立性,但也引發了對其獨立性和透明度的討論。
總結來說,聯儲在QE期間的主要購買對象是國債和抵押擔保證券,而其股東主要是美國的商業銀行,這些銀行在聯儲的運作中扮演著特定的角色。In summary, the Fed's main purchases during QE are Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities, and its shareholders are mainly US commercial banks, which play a specific role in the Fed's operations.
目前聯儲財報,若聯儲QE對資產負債表的影響細節The current Fed financial report, if the Fed's QE has any details on the impact on the balance sheet
美國聯邦儲備系統(Fed)的資產負債表在量化寬鬆(QE)政策下會發生顯著變化。以下是QE對聯儲資產負債表的影響細節:
在QE期間,聯儲會大量購買國債和其他金融資產(如房貸擔保證券)。這些購買行為直接增加了聯儲的資產規模。例如,自2008年金融危機以來,聯儲的資產負債表從不到1兆美元擴張至約9兆美元,主要是透過這些資產的購買來實現的。
由於聯儲購買資產所釋放的資金會進入市場,這會導致商業銀行在聯儲的準備金增加,從而使聯儲的負債也隨之增加。這意味著,聯儲的資產和負債會同時上升,保持資產負債表的平衡。
QE的主要目的是降低長期利率,促進經濟增長。當聯儲購買大量的國債時,這會提高這些資產的價格,並降低其收益率,進而影響整體市場利率。這種政策通常在經濟放緩或面臨衰退風險時實施,以刺激投資和消費。
QE也會影響市場對未來通脹的預期。隨著資金供應的增加,市場可能會預期通脹上升,這會影響消費者和投資者的行為。聯儲在進行QE時,通常會伴隨著對通脹的警告,以引導市場預期。
在QE期間,聯儲的資產負債表結構會發生變化,長期資產的比例上升,這使得聯儲在面對利率上升時,承擔了更大的風險。這是因為長期資產的價值對利率變化的敏感度高於短期資產。
總結來說,QE對聯儲的資產負債表有著深遠的影響,通過增加資產和負債,調整市場利率,以及改變通脹預期,聯儲能夠在經濟不穩定時期提供必要的支持。
 |
| 台灣 GDP成長率不可能超過5% |
 |
| 美元/台幣歷史圖 |
 利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool )
利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool ) 川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world )
川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world ) 2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked)
2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked) 如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? )
如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? ) 【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution )
【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution ) 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法
C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法 什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate?
什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate? 豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean
豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司
NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司 歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢
歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢何謂「海湖莊園協議」?What is the Mar-a-Lago Agreement?
 「海湖莊園協議」這個名稱,取自川普在佛州的私人度假勝地海湖莊園(Mar-a-Lago),其概念參照1985年美國與德、日、英、法簽署的「廣場協議」(Plaza Accord),當時各國協助貶值美元,促進美國經濟復甦。這項「協議」的構想,是由川普政府經濟顧問委員會主席米蘭(Miran)在去年一篇文章中提出的,當時他列舉了多種選項。如今,他已被任命為白宮經濟顧問委員會主席。The name "Mar-a-Lago Agreement" is taken from Trump's private resort Mar-a-Lago in Florida. Its concept refers to the "Plaza Accord" signed by the United States, Germany, Japan, Britain and France in 1985. At that time, these countries helped devalue the US dollar and promote the recovery of the US economy. The idea of this "deal" was proposed by Miran, chairman of the Trump administration's Council of Economic Advisers, in an article last year, when he listed a variety of options. He has now been appointed chairman of the White House Council of Economic Advisers.
「海湖莊園協議」這個名稱,取自川普在佛州的私人度假勝地海湖莊園(Mar-a-Lago),其概念參照1985年美國與德、日、英、法簽署的「廣場協議」(Plaza Accord),當時各國協助貶值美元,促進美國經濟復甦。這項「協議」的構想,是由川普政府經濟顧問委員會主席米蘭(Miran)在去年一篇文章中提出的,當時他列舉了多種選項。如今,他已被任命為白宮經濟顧問委員會主席。The name "Mar-a-Lago Agreement" is taken from Trump's private resort Mar-a-Lago in Florida. Its concept refers to the "Plaza Accord" signed by the United States, Germany, Japan, Britain and France in 1985. At that time, these countries helped devalue the US dollar and promote the recovery of the US economy. The idea of this "deal" was proposed by Miran, chairman of the Trump administration's Council of Economic Advisers, in an article last year, when he listed a variety of options. He has now been appointed chairman of the White House Council of Economic Advisers.
米蘭在文章中指出,美國龐大貿易逆差的原因是美元被高估,「這種高估使得美國出口缺乏競爭力,進口變得便宜,進而削弱美國製造業的實力。」他表示,如今像中國與歐洲這樣的重要經濟體,可能不太願意加入新的協議,但關稅可以成為有效的施壓手段。Milan pointed out in the article that the reason for the huge U.S. trade deficit is the overvaluation of the dollar. "This overvaluation makes U.S. exports noncompetitive and imports cheap, thereby weakening the strength of the U.S. manufacturing industry." He said that important economies such as China and Europe may be reluctant to join new agreements, but tariffs can be an effective means of pressure.
從Ray Dalio的觀點來看,米蘭提出的海湖莊園協議涉及多個重要的經濟議題,包括關稅政策、友邦關係、美國出口產品的競爭力、美元的霸權影響以及全球貿易的衝擊。From Ray Dalio's point of view, the Mar-a-Lago agreement proposed by Milan involves several important economic issues, including tariff policies, relations with friendly countries, the competitiveness of US export products, the hegemonic influence of the US dollar, and the impact on global trade.
米蘭博士的海湖莊園協議中,關稅政策被視為重塑美國貿易體系的核心工具之一。根據報導,米蘭認為美國的貿易逆差問題與美元被高估有關,這導致進口商品便宜而出口商品昂貴,進而影響美國的製造業和經濟結構。Dalio也指出,關稅的使用可能是為了減少對外國生產的依賴,這在當前的全球經濟環境中尤為重要。但等於是美國主動離開全球自由貿易形成高關稅保護國家,其他國家仍在全球自由貿易,將造成國際化的美商分成國際分公司、美國本土公司獨立營運,美國的農產品、能源、原物料出口至其他沒有對美國報復關稅國家將增加,美國進口商品漲價,也無法增加美國工業產品競爭力。In Dr. Milan’s Mar-a-Lago agreement, tariff policy is seen as one of the core tools for reshaping the U.S. trade system. According to reports, Milan believes that the US trade deficit problem is related to the overvalued dollar, which makes imported goods cheap and exported goods expensive, thus affecting the US manufacturing industry and economic structure. Dalio also noted that the use of tariffs could be an effort to reduce reliance on foreign production, which is particularly important in the current global economic environment. But this is equivalent to the United States voluntarily leaving global free trade and becoming a country with high tariff protection, while other countries are still engaged in global free trade. This will cause internationalized American companies to be divided into international branches and American domestic companies to operate independently. The export of American agricultural products, energy, and raw materials to other countries that do not impose retaliatory tariffs on the United States will increase, and the prices of American imported goods will increase, which will not increase the competitiveness of American industrial products.
海湖莊園協議的實施可能會對美國的友邦關係產生影響。Dalio 提到,當美國推行保護主義政策時,可能會導致與主要貿易夥伴的緊張關係,這不僅影響經濟合作,也可能引發更廣泛的地緣政治衝突。這種情況下,友邦國家可能會對美國的貿易政策感到不安,進而影響雙邊貿易的穩定性。The implementation of the Mar-a-Lago agreement may have an impact on America’s relations with friendly countries. Dalio mentioned that when the United States pursues protectionist policies, it may cause tensions with major trading partners, which will not only affect economic cooperation but may also trigger broader geopolitical conflicts. In this case, friendly countries may feel uneasy about the US trade policy, which in turn affects the stability of bilateral trade.
米蘭博士的報告強調,美元的高估使得美國的出口產品在國際市場上失去競爭力。Dalio 認為,這種情況如果不加以改善,將會進一步削弱美國的經濟基礎,特別是在製造業方面。米蘭提出的解決方案之一是促使美元貶值,以提高美國出口產品的價格競爭力,這一點與 Dalio 的觀點相呼應。Dalio 觀點,美國競爭力必須從基礎去努力:Dr. Milan's report emphasized that the overvaluation of the dollar has made US exports uncompetitive in the international market. Dalio believes that if this situation is not improved, it will further weaken the economic foundation of the United States, especially in the manufacturing sector. One of the solutions Milan proposed was to weaken the dollar to make U.S. exports more price competitive, a point echoed by Dalio. Dalio believes that the US must work on its fundamentals to improve its competitiveness:
海湖莊園協議的另一個重要方面是美元的霸權地位。米蘭博士認為,美元作為全球主要儲備貨幣的地位使其被高估,這對美國經濟造成了長期的負擔。Dalio也指出,美元的強勢可能會導致其他國家尋求替代貨幣,這將對全球金融體系造成深遠影響。這種情況下,美國需要重新評估其貨幣政策,以維持美元的全球地位。關稅拉高、配合弱勢美元,可能造成美元國債投資人疑慮,升高美國國債殖利率降低美國國債安全性。Another important aspect of the Mar-a-Lago agreement is the hegemony of the U.S. dollar. Dr. Milan believes that the dollar's status as the world's main reserve currency makes it overvalued, which poses a long-term burden on the US economy. Dalio also pointed out that the strength of the U.S. dollar could lead other countries to seek alternative currencies, which would have far-reaching implications for the global financial system. In this situation, the United States needs to reassess its monetary policy to maintain the global status of the dollar. Higher tariffs, coupled with a weaker dollar, could cause concerns among U.S. Treasury investors, raising U.S. Treasury yields and reducing the security of U.S. Treasury bonds.
米蘭博士的報告中提到,美元的高估使得美國的出口產品在國際市場上失去競爭力。Dalio認為,這種情況如果不加以改善,將會進一步削弱美國的經濟基礎,特別是在製造業方面。他指出,中國在全球貿易中的地位不斷上升,這使得美國必須重新評估其貿易政策,以維持競爭力。Dalio建議,應該考慮讓人民幣對美元升值,這可以通過中國出售美元資產來實現,並同時刺激內需,這樣的策略將有助於改善中美之間的經濟不平衡。中國影響:Milan's report mentioned that the overvaluation of the US dollar has made US exports noncompetitive in the international market. Dalio believes that if this situation is not improved, it will further weaken the economic foundation of the United States, especially in the manufacturing sector. He noted that China's growing role in global trade requires the United States to reassess its trade policies to remain competitive. Dalio suggested that consideration should be given to allowing the RMB to appreciate against the U.S. dollar, which could be achieved by China selling its U.S. dollar assets and stimulating domestic demand at the same time. Such a strategy would help improve the economic imbalance between China and the United States. Chinese influence:
最後,海湖莊園協議的實施可能會對全球貿易格局造成重大衝擊。Dalio警告,當前的貿易政策不確定性加劇了市場的波動,並可能導致全球經濟的動盪。米蘭的報告中提到的各種政策選項,如發行百年期債券和建立主權財富基金,都是為了應對這些挑戰,但其實施的可行性和效果仍然存在爭議。Finally, the implementation of the Mar-a-Lago agreement could have a significant impact on the global trade landscape. Dalio warned that current trade policy uncertainty has increased market volatility and could lead to turmoil in the global economy. The various policy options mentioned in the Milan report, such as issuing 100-year bonds and establishing sovereign wealth funds, are intended to address these challenges, but their feasibility and effectiveness remain controversial.
總結來說,從Ray Dalio的觀點看,米蘭博士的海湖莊園協議提出了一系列旨在重塑美國經濟和貿易政策的措施,這些措施的成功與否將直接影響美國的經濟競爭力及其在全球貿易中的地位。In summary, from Ray Dalio’s point of view, Dr. Milan’s Mar-a-Lago Agreement proposes a series of measures aimed at reshaping the US economic and trade policies. The success or failure of these measures will directly affect the US economic competitiveness and its position in global trade.
綜合分析
 利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool )
利用雲端數學工具計算Z轉換及Z反轉換 ( Calculate Z transform and inverse of Z transform by cloud math online tool ) 川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world )
川普經濟學將成為全球重要趨勢,台灣還在停滯 ( Donald Trump's Economic will become the new trend to world ) 2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked)
2018 高房價超級泡沫出現裂痕,中美貿易戰持續,中國消費拉響警報 (2018 China's consumption alarm, China-US trade war continued, high housing price super bubble cracked) 如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? )
如何攝取足夠微量元素營養,來防止慢性病? ( How to get enough micronutrients to prevent chronic diseases? ) 【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution )
【新腦內革命:春山茂雄71歲,擁有28歲青春的不老奇蹟】研讀心得: 肥胖主因是生長荷爾蒙的分泌量驟降 ( The secretion of growth hormone dips is the main cause of aging and obesity - Brain Revolution ) 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得
【驚人的血管彈力操】及【血管老化,當然會中風:5種食物,7招保健操,血管變年輕】 - 讀書心得 C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法
C++ 教學 fread( ) 用法 什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate?
什麼是 MP4 串流及資料量? ( what is the MP4 streaming and its streaming rate? 豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean
豆腐乳結合酵素及益生菌,營養減肥又好吃 ( Fruits with fermented bean NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司
NVIDIA 進入 AI 高速成長時代的 AI 創新公司,INTEL 成為傳統產業半導體公司 歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢
歐美市場將期待 TESLA MOTOR HOME (移動房屋),是房屋新趨勢